What is ClientRects

Hello, dear friends. Today we will talk about such a browser fingerprint as Client Rects. Users first started talking about this fingerprint in 2016 after the first basic and simple option to check it appeared on the Browserleaks checker. At that time, its substitution did not seem difficult. But implementing the most natural substitution and eliminating the possibility of its detection is not as easy as it seems at first glance. Until now, most popular solutions on the market cannot competently and efficiently substitute this fingerprint.
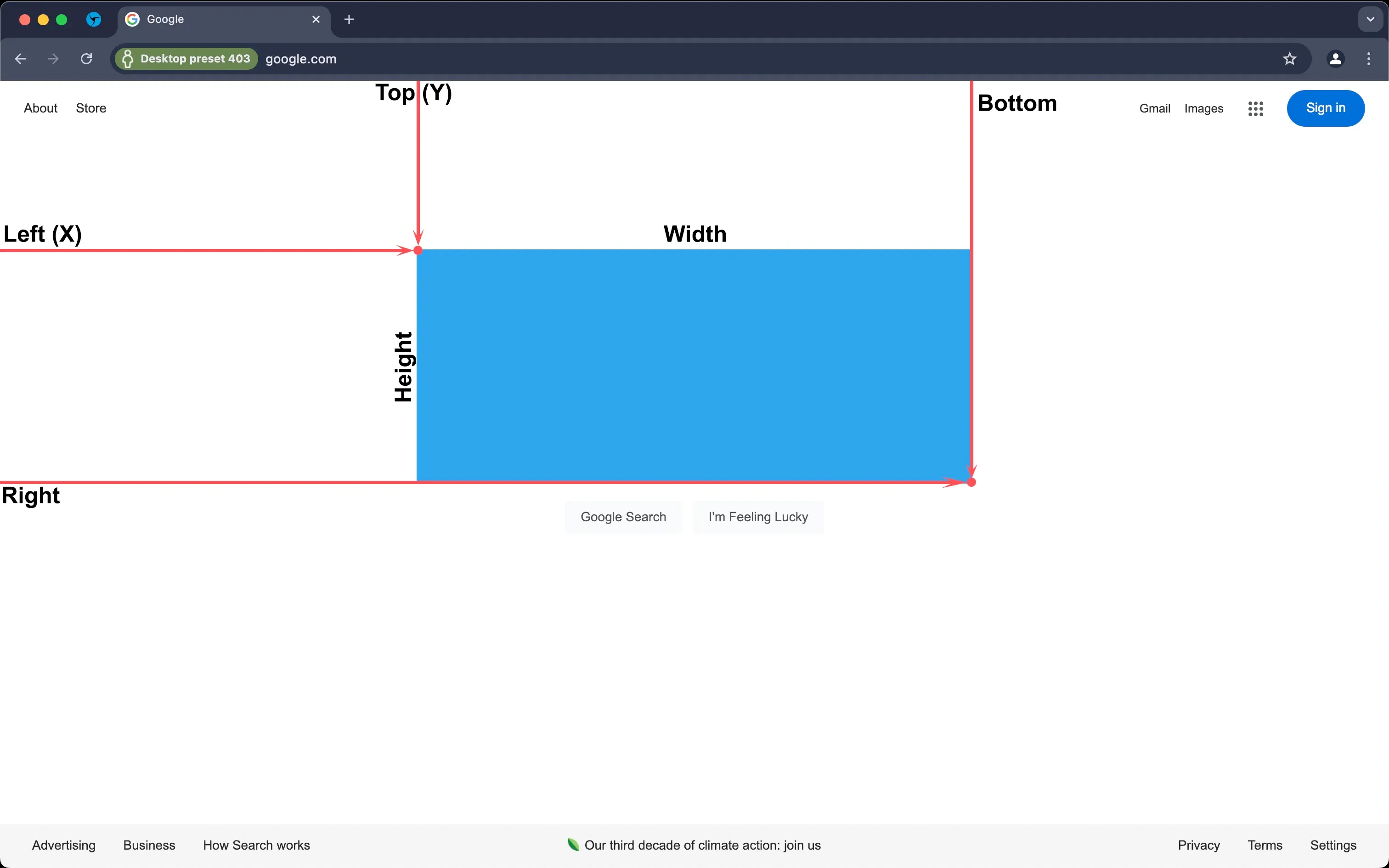
First, it is worth telling what Client Rects is in simple terms. Client Rects is a technology in the browser that allows you to get information about the location and size of web page elements.
The elements can be different: a text field, a button, a drop-down list, a table and many other HTML objects.
The size information includes the width and height of the element in pixels.
The position information includes the coordinates of the element's top-left point (left or X; top or Y) and bottom-right points of the object (right and bottom) relative to the visible area of the web page in the browser (viewport).
The collection of this information is called "rectangles" (rects). You can see it more clearly in the image below.
Now let's look at the checker https://browserleaks.com/rects in order to analyze in more detail how the Client Rects fingerprint is obtained.
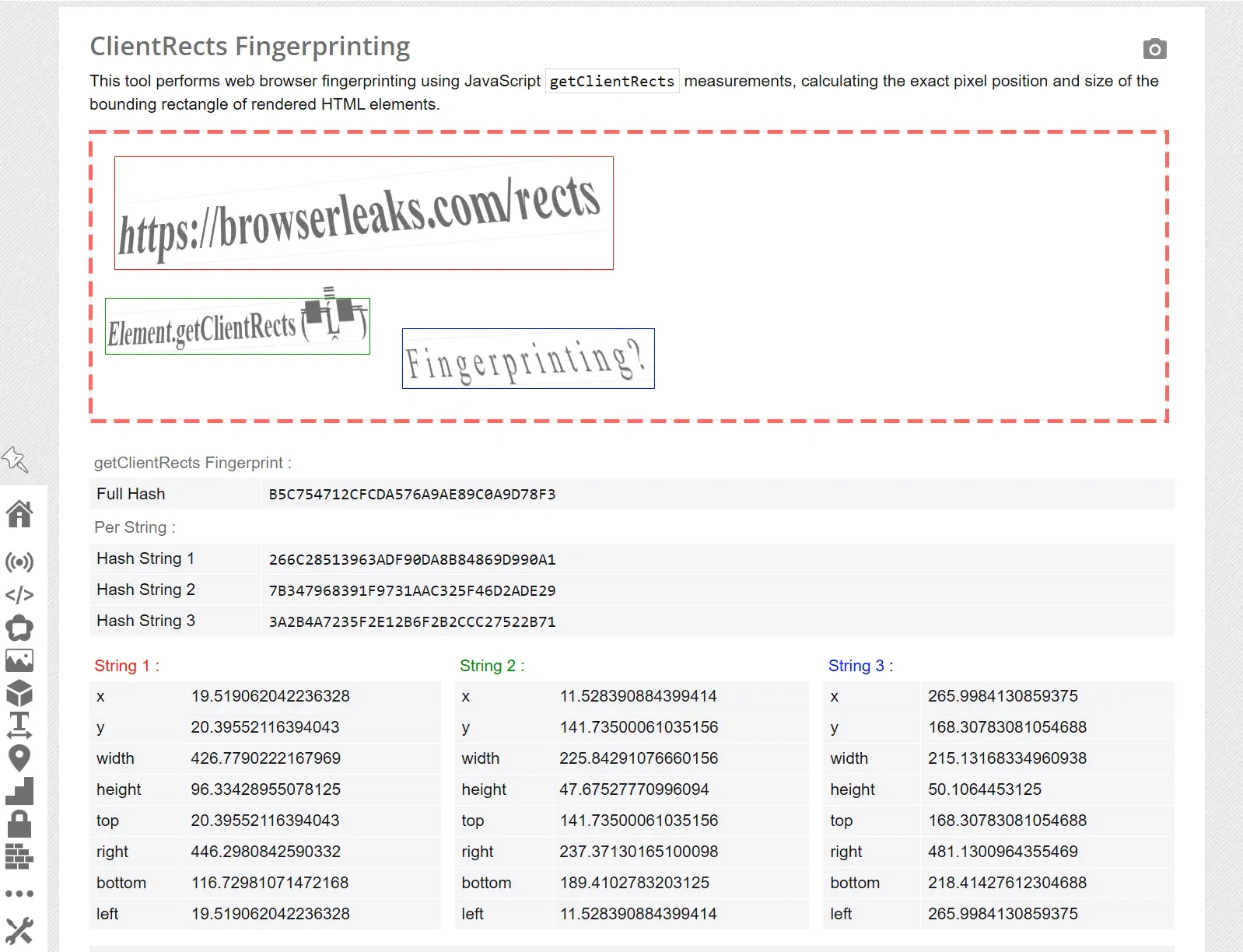
This site uses three elements to create a fingerprint (String 1, String 2, String 3). After you open the checker page, browserleaks gets information about the size of these elements (width, height) and the coordinates of these elements (x/left, y/top, right, bottom) in pixels relative to the dotted frame. As you can see, the values of the parameters of the elements are not rounded to integers, but are provided with a maximum accuracy of up to 16 digits after the point.
After receiving the necessary data on these three elements, browserleaks processes the information for each element, converting it into a hash (Hash String 1, Hash String 2, Hash String 3). Then the checker uses these three hashes and converts it into one (Full Hash), which can already be designated as the Client Rects fingerprint.
Of course, this is one of the simplest examples of how to remove the Client Rects fingerprint. For example, the checker https://privacycheck.sec.lrz.de/active/fp_gcr/fp_getclientrects.html uses a slightly more complex scheme to obtain a fingerprint, using a larger number of html elements of different types. Modern anti-fraud systems can use much more complex schemes to obtain this fingerprint, compare your fingerprint with their personal database, combine it with other fingerprints, parameters, IP addresses to identify the user and protect against multi-accounting.
The main reason why anti-fraud systems can use this fingerprint to prevent multi-accounting, tracking and identify the user is small differences in the results of the parameter values on different devices. If you open the Client Rects checker web page on two different PCs, the three elements will visually look identical, but the parameter values of each element will differ, and therefore all 3 Hash String and Full Hash will have different values. Any change in values, even one hundred thousandth of a pixel, can change your fingerprint.
An example of a Client Rects fingerprint on two different Windows 10 computers in the Google Chrome browser:
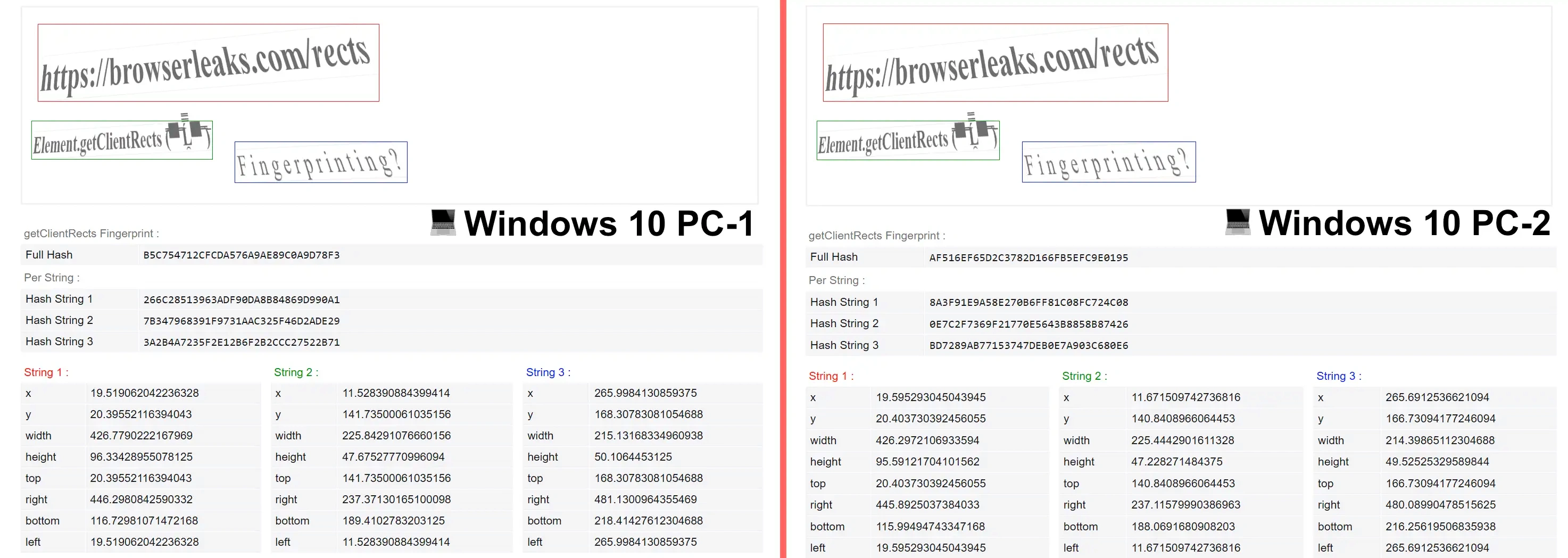
A logical question arises: what "variables" can affect the fact that two different devices can display parameter values with a slight difference? The answer is simple - many! Device type, operating system, operating system version, videocard, monitor, screen resolution, scale in the system, browser type, browser version, browser page zoom, fonts - these are the most basic "variables" that can affect the parameter values, and therefore the fingerprint as a whole.
Let's look at a sequential example in the context of the Google Chrome browser: we use a mobile device - we have one fingerprint, we use a laptop - we have a different fingerprint. We connect a 2K monitor, and then 4K - the fingerprints will be different. We change Windows 10 to Windows 11 - the fingerprint will change, we change the Windows scale in the system from 100% to 125% - the fingerprint also changes, we launch the browser through the built-in Intel laptop video card - one fingerprint, we launch it through a discrete video card - another fingerprint. And so on.
Example of Client Rects fingerprint in Windows 10 Google Chrome with different scaling:
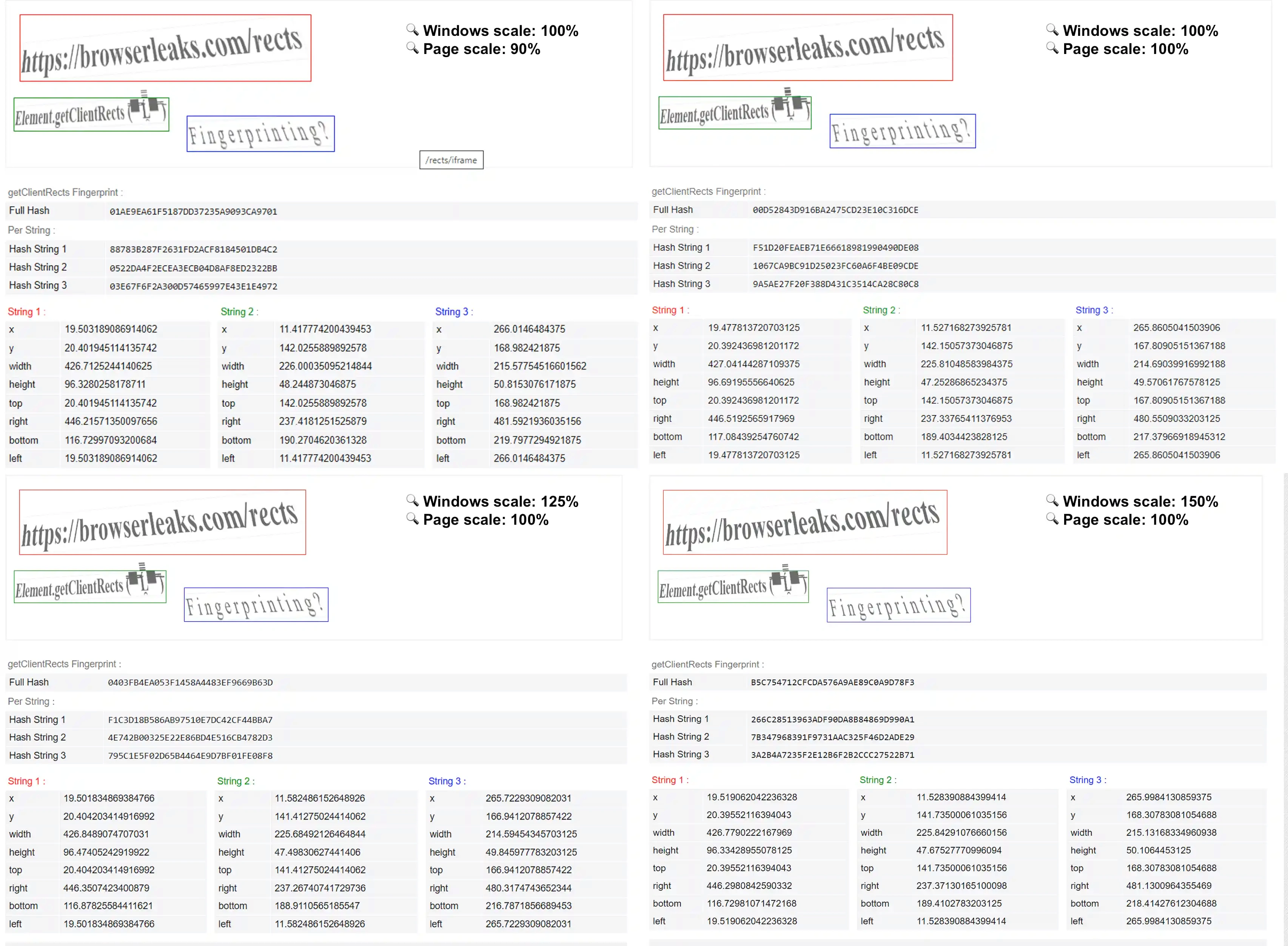
Of course, if you create tens, hundreds or thousands of accounts per month, running to the store buying up various devices, monitors and videocards, reducing the scale of the browser page to such a size that without a magnifying glass it will be impossible to see anything on the monitor screen is far from the best idea for obtaining a unique fingerprint. The best solution in this case would be to use a technological anti-detect browser with a high-quality substitution of this fingerprint.
There are two main methods for substituting the Client Rects fingerprint: using add-ons or extensions in the browser and using an anti-detect browser. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Using add-ons or extensions in the browser is the easiest way to substitute a fingerprint. But it has several significant drawbacks:
-
The ability to detect an extension or add-on. User identification methods allow you to determine which extensions and add-ons are installed on the user. If the corresponding add-ons are detected, a red flag is provided to you in front of a modern anti-fraud system.
-
Low quality of fingerprint substitution. Substitution technologies used in such extensions and add-ons leave much to be desired. The lower the quality of the substitution, the higher the chance of the anti-fraud system detecting it.
-
Using blocking instead of substitution. Some browser add-ons can use Javascript blocking or Client Rects technologies. The worst case scenario. In addition to detection, the browser can display web page elements “crookedly” due to blocking. In this case, you can forget about correct work with some websites.
This method can be used only as one of the links in the chain of security and anonymity, but not for work or multi-accounting. Popular add-ons for substitution in Mozilla Firefox: CanvasBlocker, Trace, Chameleon; extensions for Google Chrome: ClientRects Fingerprint Defender, Trace.
Using an anti-detect browser is the best method for substituting the Client Rects fingerprint. But do not rush to use the first product that comes to hand, there is no need to rush in this matter. It is important to choose the right software that will allow you to get the best result of substitution.
Basically, extensions and anti-detection browsers add salt, noise (i.e. invisible pixels) to the calculations of Client Rects, thereby slightly adjusting the sizes of the final elements, which leads to the detection of the fingerprint by anti-fraud systems in 10 out of 10 cases.
The new generation of Linken Sphere uses a completely different substitution method based on the technology of built-in zooming, which allows you to get an ideal substitution in 8 out of 10 sessions.
In some cases, to assess the quality of fingerprint substitution, you do not need to be an expert in the field of anti-fraud systems, it is enough to simply compare the results from a regular browser and anti-detection by checker.

The screenshot above shows the results of the check on the Browserleaks website in a regular Google Chrome browser, Linken Sphere 2 and one of the popular anti-detect browsers on the market. It is clear to the naked eye how incorrectly the elements are displayed due to the fingerprint substitution using noise.
Also, to check the quality of the substitution, we can recommend a checker such as CreepJS. Unlike other services for checking the Client Rects fingerprint, this website allows you to evaluate its quality of substitution. To do this, with the substitution enabled, look in the "Browser" section for the "lies" item.
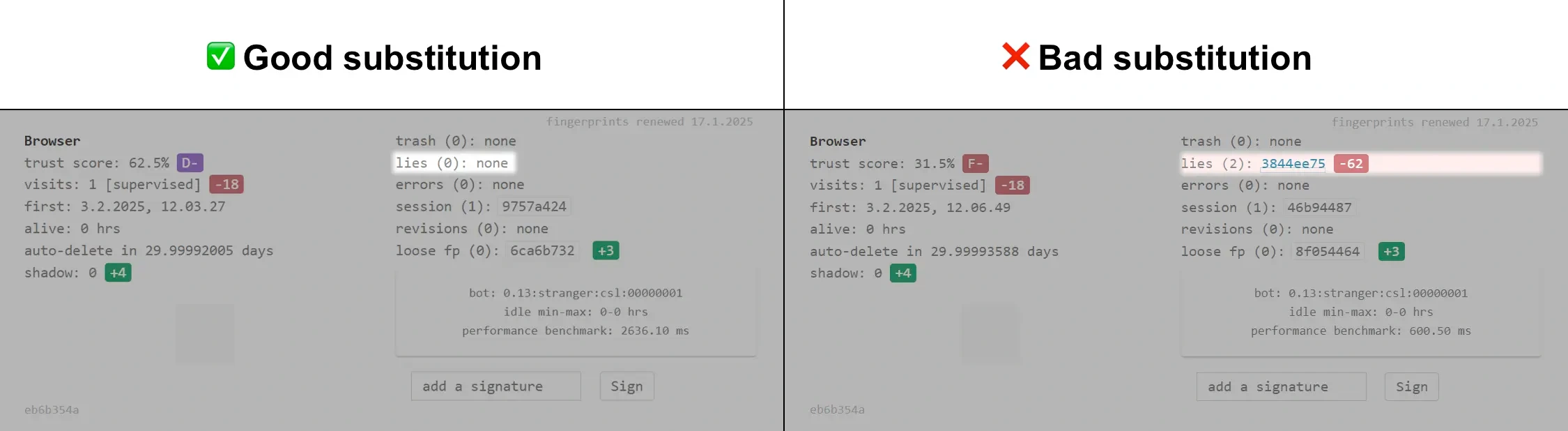
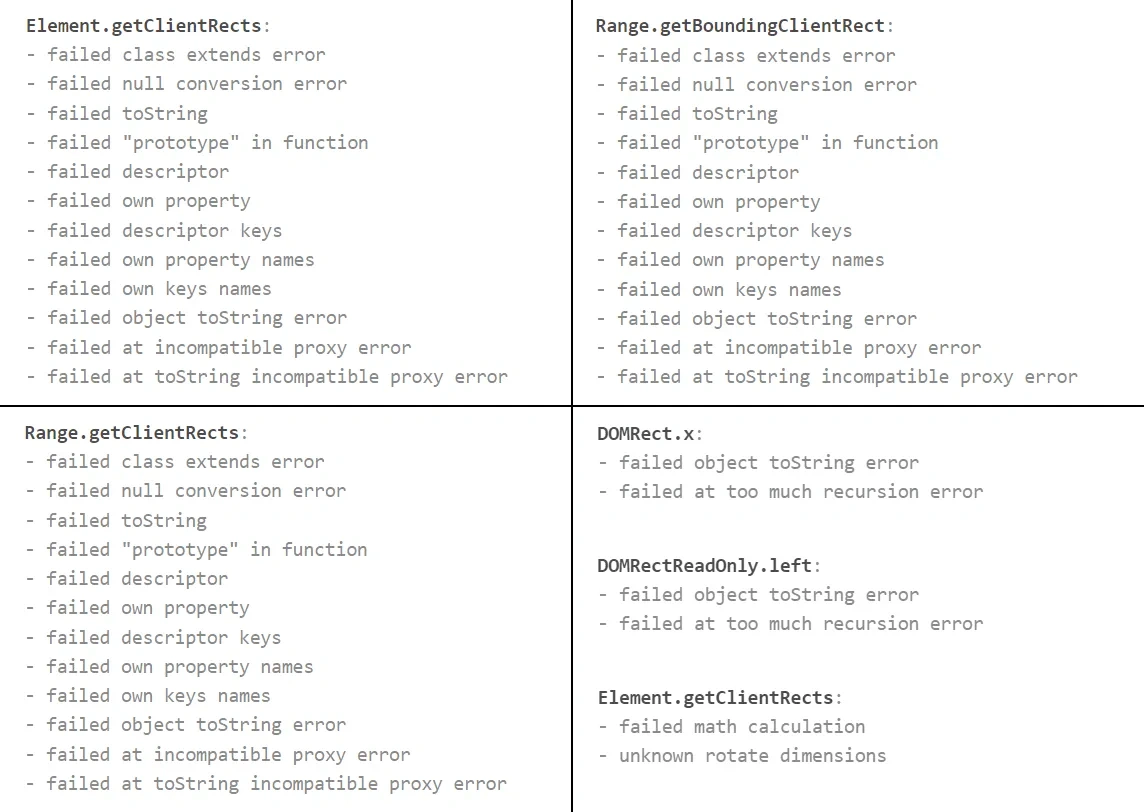
The "lies" parameter must have the value "none" as on the left in the screenshot above. When a substitution is detected, this item will be highlighted, and the number of errors will be indicated in brackets. In this case, when you click on the lies value, you can view these errors in more detail. When a substitution is detected, errors will be in functions such as "Element.getClientRects:", "Range.getClientRects:", "Range.getBoundingClientRect:", "DOMRect.height:", "DOMRectReadOnly.top:" etc.
An example of errors when detecting a substitution of Client Rects:
Now let's compare the results on CreepJS with substitution enabled in Linken Sphere 2 and in another similar product:
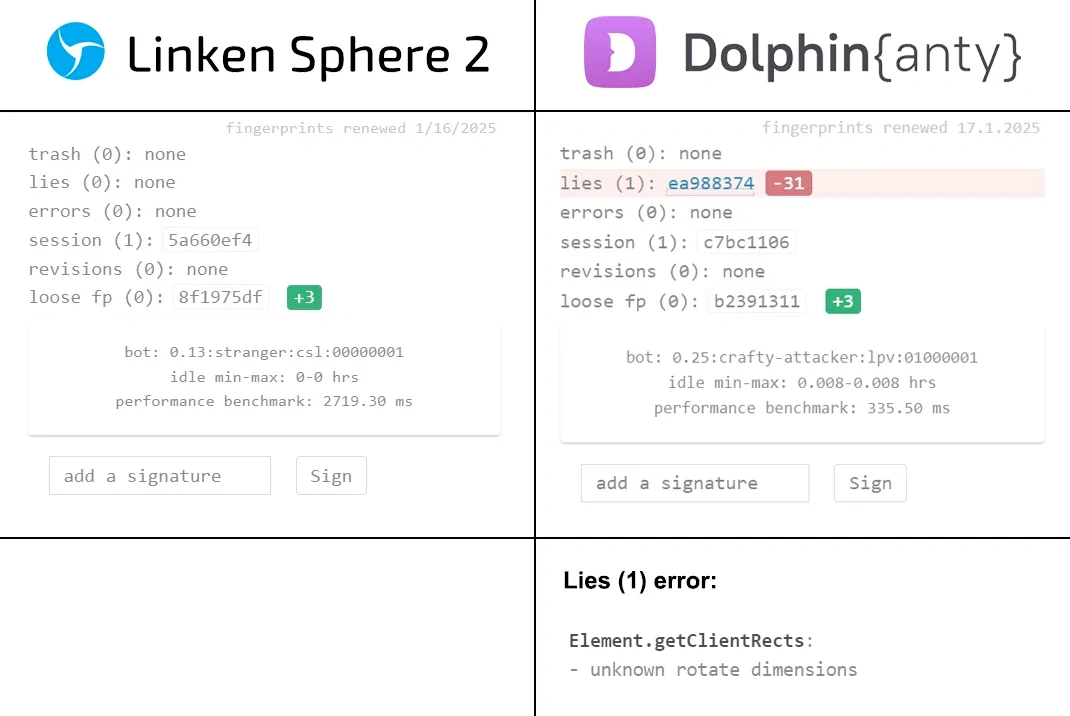
It is easy to see how this checker can easily detect the Client Rects fingerprint substitution, while Linken Sphere doesn't have any problems with detection.
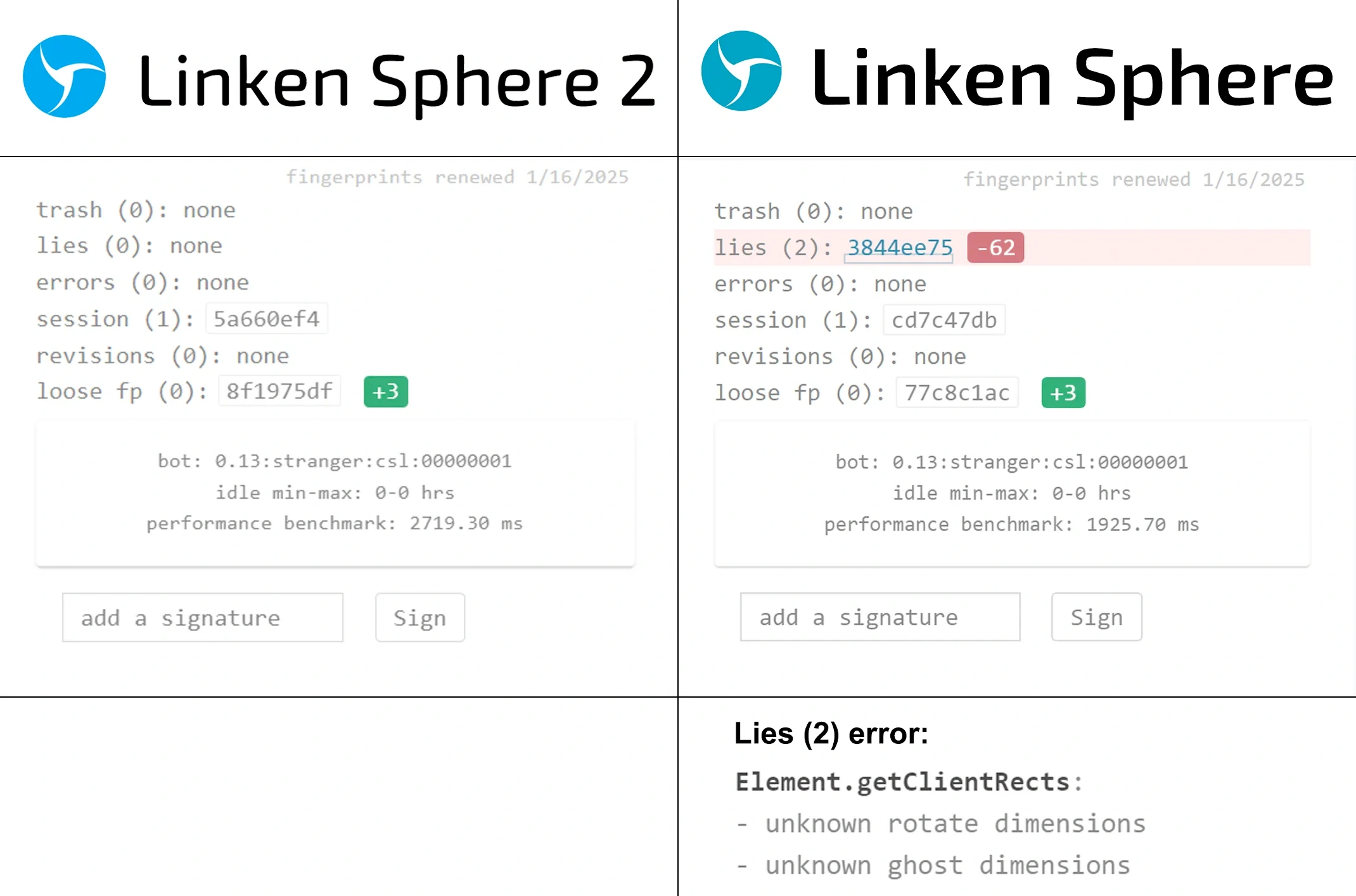
But it would be unfair and impartial not to mention that in the previous generation of Linken Sphere, the implementation of the Client Rects fingerprint substitution was far from ideal. For this reason, support recommended that you do not use it unless absolutely necessary.
Comparison of fingerprint substitution in Linken Sphere 2 and Linken Sphere 9:
To sum up the above, it should be noted that it is important not just to replace the fingerprint so that it is unique. It is important to do it qualitatively, and so that its substitution can't be detected. To do this, you need to use a product that has modern technological and innovative solutions in the field of substitution. And then the result of your work will not take long to come!

